How Does Tattoo Work
How Does Tattoo Work - A tattoo is forever (ish). Web the process of tattooing essentially creates an open wound, and your body responds as such. Web tattoos & piercings. This can be between fifty and three thousand times per minute. A tattoo is a permanent form of body modification where an artist injects inks and pigments (dyes) into your skin. The machine has needles that pierce the skin many times. Although many people can and do get tattoos successfully removed, there’s no guarantee that these methods will always work. Web tattoos have been around for thousands of years—but how do they work? Tattooing causes a small amount of bleeding and some pain. Tattooing is the process of injecting ink into the skin to make permanent images. The ink is injected into the dermis by a machine that delivers thousands of tiny pricks per minute via needle. Web most tattoo studios use a machine called a thermal imager to make their stencils. This can be between fifty and three thousand times per minute. But one thing’s for certain: Most notably, au fa’atala or au mono (used for. According to the american chemical society, modern tattoo needles puncture the skin at 50 to 3000 times per minute, going through the epidermis, the outer. Web tattoo physics part 1 | tattoo overview | episode 8. Tattoo healing stages length of healing process tattoo healing and aftercare. What to expect from the tattoo healing process: That's creating trauma as well. Tattoo removal is a procedure to remove this permanent ink from your body. Brought to you by inside. So, as you admire the intricate designs adorning the skin, remember that each tattoo is not merely an artwork—it’s a story etched into the living canvas of human. Web the art of creating the tattoo. In fact, the oldest decorative skin markings. Understanding the tattoo process is essential, as it helps you become more comfortable and calm while getting your first tattoo. Tattooing causes a small amount of bleeding and some pain. So, as you admire the intricate designs adorning the skin, remember that each tattoo is not merely an artwork—it’s a story etched into the living canvas of human. With every. To do this, they use an electrically powered tattoo machine that resembles (and sounds like) a dental drill. Tattoo healing stages length of healing process tattoo healing and aftercare. The epidermis, the dermis, and the subcutaneous layer. They add color to your tattoo, if applicable. These cells eat up the ink and actually keep it within their cellular membranes which. Artists apply tattoo ink using a specialized mechanical machine operated by a foot pedal. This saves hours of tracing time; The tattoo machine has an electric motor, and some people have said it sounds to them like a dental drill. Tattooing is the process of injecting ink into the skin to make permanent images. Brought to you by inside. A tattoo is forever (ish). Web tattoos / tattoo designs / tattoo process explained: Web during tattooing, a needle is puncturing the skin at anywhere from 50 to 3,000 times per minute. Since the neolithic era, people have been getting tattoos. Web the art of creating the tattoo. This saves hours of tracing time; With every puncture, the needles insert tiny drops of ink into the top layer of the skin. That's creating trauma as well as injecting a foreign substance into the. Laser tattoo removal uses pulses of light directed at your skin to remove unwanted tattoos. Traditionally, tattooing often involved rubbing pigment into cuts. With every puncture, the needles insert tiny drops of ink into the top layer of the skin. Since the neolithic era, people have been getting tattoos. The tattoo machine has an electric motor, and some people have said it sounds to them like a dental drill. Web how do tattoos work? Tattoos are permanent images that pigments create on our. This tissue is just underneath the outer layer of your skin, called the epidermis. They'll simply insert your tattoo design into the machine and it'll transfer onto a special thermal paper in seconds. Your artist will outline the design on the skin. Web the skin is divided into three layers: The artist shades the tattoo. Web basically, ink is implanted into a person’s skin. Brought to you by inside. Tattooing is the process of injecting ink into the skin to make permanent images. The epidermis, the dermis, and the subcutaneous layer. Web in the case of tattoos, the macrophages see the ink as foreign. This tissue is just underneath the outer layer of your skin, called the epidermis. Since the neolithic era, people have been getting tattoos. Web usually, a tattoo artist uses a handheld machine that acts much like a sewing machine. Dec 17, 2023 1:29 pm est. In fact, the oldest decorative skin markings found in human remains date back to 6000 b.c. A tattoo is forever (ish). Get detailed information through pictures and explanation on how it all works. The needle moves up and down up to 3000 times per minute. The tattoo artist uses a needle to insert ink into the skin. According to the american chemical society, modern tattoo needles puncture the skin at 50 to 3000 times per minute, going through the epidermis, the outer. Web how do tattoos work?
This Is How Tattoo Machines Work In Slow Motion Cyprus International

How Do Tattoos Work? — Certified Tattoo Studios

Tattoo Process Explained Step By Step Thoughtful Tattoos
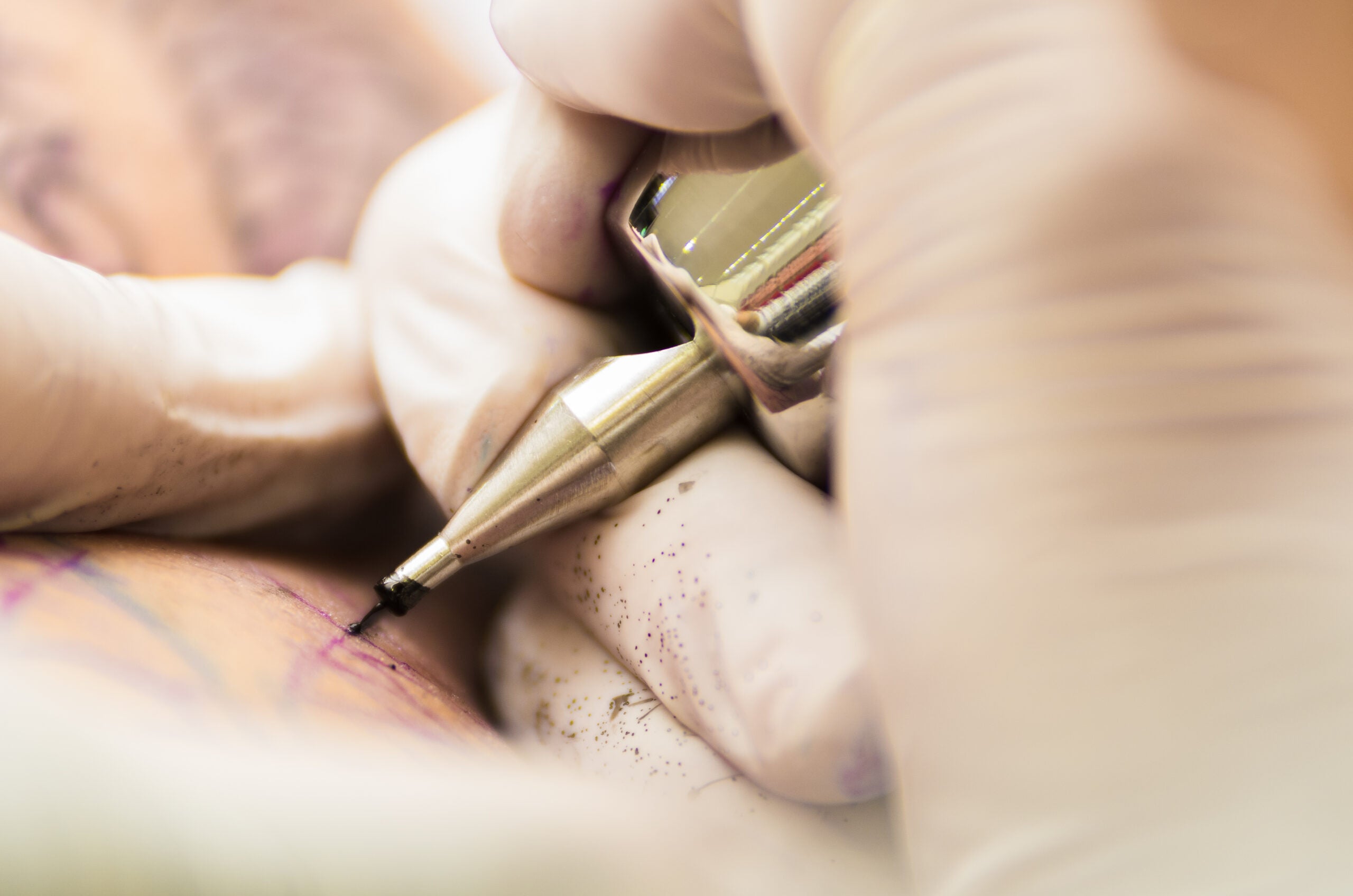
Tattoos are permanent, but the science behind them just shifted

Tattoo Process Explained Step By Step Thoughtful Tattoos

How Do Tattoos Work? Quick Guide to the Science of Tattoos
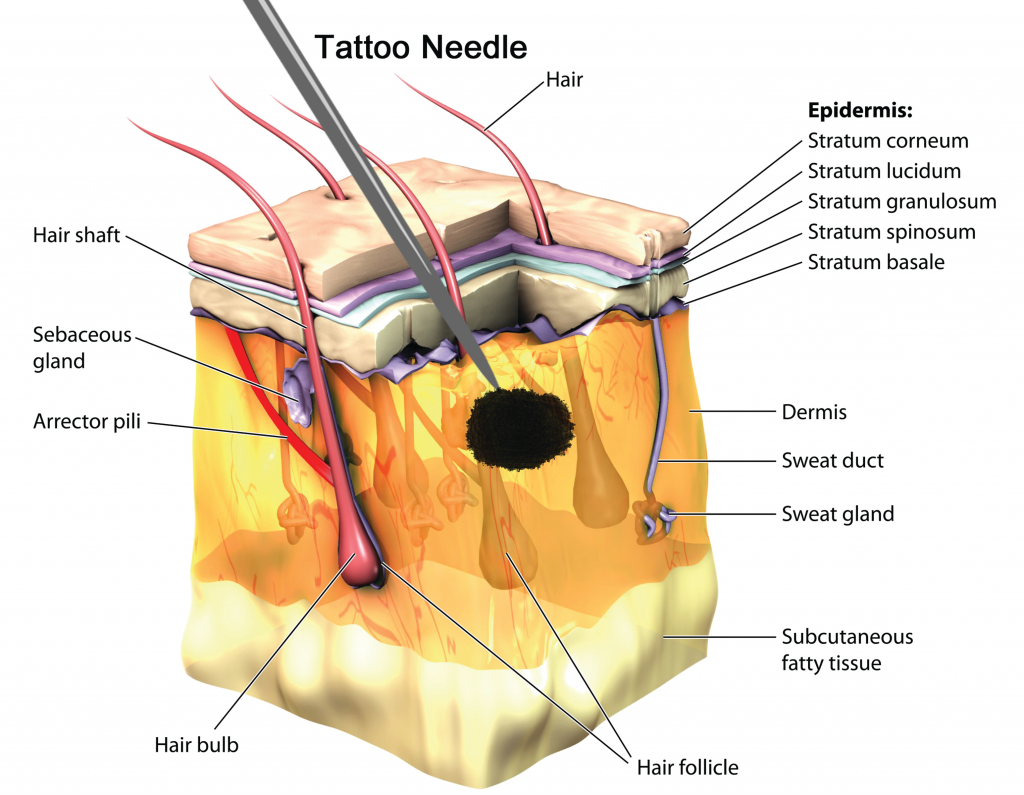
Before You Get a Tattoo, Know About Its Ink Ingredients! Procaffenation

How Do Tattoo Machines Work? FREEYORK

How Tattoos Work THE WORLD FAMOUS

How Do Tattoos Work? Your Ultimate Guide to the Tattoo Process
Web Getting A Tattoo Is A Three (Or Four) Step Process:
They'll Simply Insert Your Tattoo Design Into The Machine And It'll Transfer Onto A Special Thermal Paper In Seconds.
It Sends Cells To That Area To Try And Clear The Foreign Substance (Ink), But Become Trapped In The Dermis Because The Ink Particles Are Too Large To Disperse.
Tattoos Are Permanent Images That Pigments Create On Our Skin.
Related Post: